Modeling Steps
The steps of creating a common model in OpenSRANE has been shown in the following figure. There is an emphasize on the common model because when user understood the way that OpenSRANE creates the models, then without following the below steps, user can create his desired model in different way!
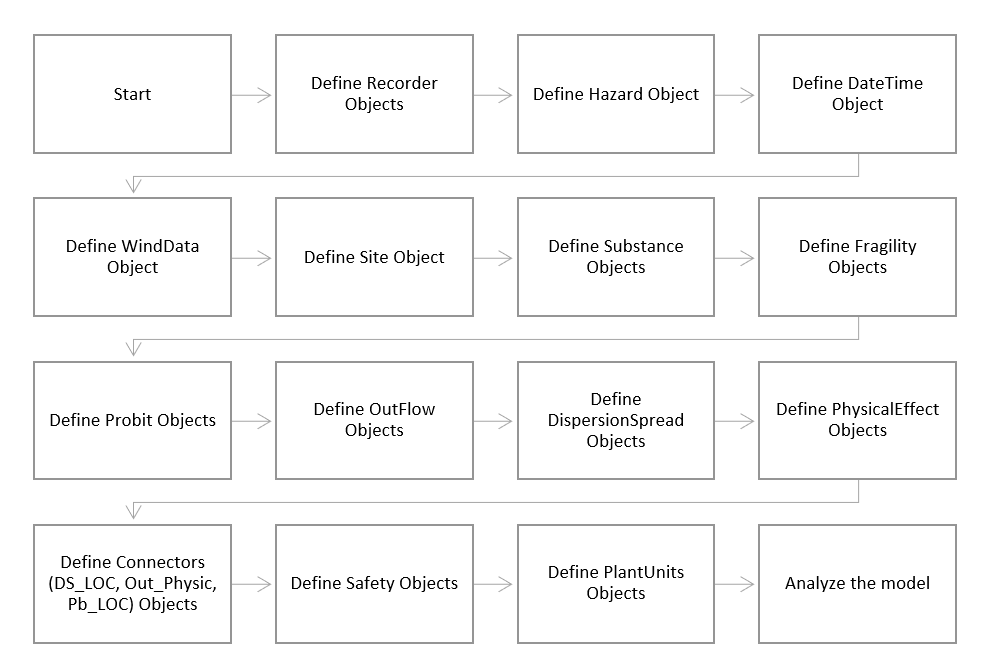
Modeling Steps
Note
for a complete modelling user should pass the steps shown above to finish the model. For each step user can uses Python coding commands and features (loops commands, dictionaries, lists …) to make modeling more convenient and it depends on the user. But before start of the analysis, the required objects shown in the following path should be defined.
Warning
To know and use the commands in a programming language in order to develop an application (coding) is one thing. To program in a language is something different. Programming involves creativity and thinking at a higher level, thinking in terms of problem solving, what are the abstractions and algorithms that can be employed to solve the problem. Programmers finally use code to express their thoughts of how to solve the problem. All programmers are coders. Most coders are NOT programmers. To utilize the OpenSees interpreters effectively YOU WANT TO BECOME A PROGRAMMER.
This warning has been hired from OpenSees Documentation page. OpenSRANE users also should pay attention to this warning before using OpenSRANE.
Linked Modeling Steps
In the following, the steps that showed in the Modeling Steps will be explain more and the related document page is linked for more convenient users access.
- Start:
To start modeling it is highly recommended that using wipe command clear all defined objects that may exist in the memory.
- Define Recorders:
To save the analysis results it is important that user using one of the existing recorders methods in Recorders, define the recorder/s objects and in this way the way of recording results will be specif y for the software.
- Define Hazard:
Usign Hazard subpackage, user should define hazard curve for the software. Currently earthquake command exist and user could define seismic hazard curve for software.
- Define Date And Time:
User should also define the time and date model for software. Usign DateAndTime subpackage, user could define Date and time model for the software.
- Define WindData:
To define site wind date, Usign WindData subpackage, user could define Wind model for the software.
- Define Site data:
To define site properties, the Sites subpackage has been provided.
- Define Substance/s:
The material that fill plant units should be define using Substance.
- Define Fragilities:
Using Fragility command, user could define all plant units possible fragilities.
- Define Probits:
To define vulnerability of plant units and also NodesGroup objects, Using Probit command, user could define the required probits.
- Define OutFlow models:
Materials outflow from damaged plant units should be model using existing models or commands in the OutFlowModel subpackage.
- Define Dispersion and spread models:
To define the models related to dispersion and spread of outflowed materials, the DispersionSpreadModels subpackage has been provided.
- Define Physical effect models:
The PhysicalEffect subpackge is responsible for defining physical effect models and using this subpackage user can define various physical effect models.
- Define Connectors:
The defined models like outflow models, DispersionSpread models and PhysicalEffect models should properly connect to related plant units. But it is not necessary to define them directly. Using Connectors subpackage user can connect mentioned models to each other with desired occurrence probability.
- Define Safety OBjects:
Safety Objects can be define using commands exist in Safety subpackage.
- Define Plant Units:
The final part of modeling is defining plant units using PlantUnits subpackage. Each command in this subpackage is related to a type of Plant unit.
- Analysis:
By defining the plant units, the model is now ready for analysis. In Analyze subpackage there are various methods to run the analysis.
Other existing Subpackages
There are some packages that using of them is not necessary, however they maybe become useful for completing the analysis. In the following they are explained and linked to their documentation page.
NodesGroup (Vulnerable Objects):
Plotting tools:
It is really convenient to check the model and results visually. Using Plot subpackage, user have access to some provided commands to plot various defined objects.
Access to Objects:
By finishing the analysis, it is important to have access to object to check their results and condition. To way of access to defined objects or elements is described in This Page.
Objects or Elements data:
By referring or accessing to an element or object, various data can be read from them. The data that can be read from an object is described This Page. For each object there are various data that can be read.
PostProcess Subpackage:
There is also a subpackage that is provided for post processing. But there is no mandatory to use this subpackage. To use this subpackage user should first load data and then call the existing desired results. Also, some auto plots is available. All required knowledge to use it, is described in This page.
figure/s by: Bijan Sayyafzadeh